Plant PartsYou probably know that plants have different parts like roots, stems, leaves, and sometimes flowers. Each part has a special job to do. For instance, the roots soak up water and nutrients, like nitrogen, from the soil. The stem carries these important things up to the leaves. Speaking of leaves, that's where the real action takes place.
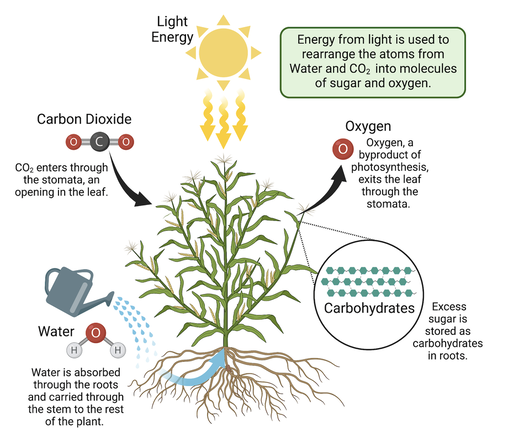
Inside the leaves, there are special cells that work together to help the plant do something called photosynthesis. This is how plants are unique compared to animals. While animals have to eat to get food, plants can make their own food through photosynthesis. In the stem, there are two types of transport cells called xylem and phloem. These cells create tubes in the stem to move different things around. The xylem moves water and minerals, while the phloem carries sugar. Inside the leaves, there are more special cells. Some of these cells can open and close to let gases in and out. They're called guard cells, and they control tiny openings in the leaf called stomata. When these openings are open, carbon dioxide and oxygen can go in and out, and water vapor can escape. Also in the leaves, there are cells with lots of chloroplasts, which are tiny parts that help the plant do photosynthesis. These special cells are called palisade cells. Inside chloroplasts, there's something called chlorophyll, a green substance that grabs light from the sun to help with photosynthesis. |
|
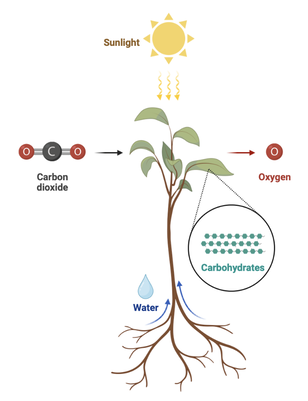
PhotosynthesisPlants perform photosynthesis in specialized organelles called chloroplasts. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light from the sun. Inside the chloroplast the light energy is used to make the high energy, carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, in glucose. The atoms needed to make glucose come from the air. Carbon dioxide in the air is used for the carbon in glucose. The oxygen in glucose also comes from the carbon dioxide. The hydrogen in glucose comes from water.
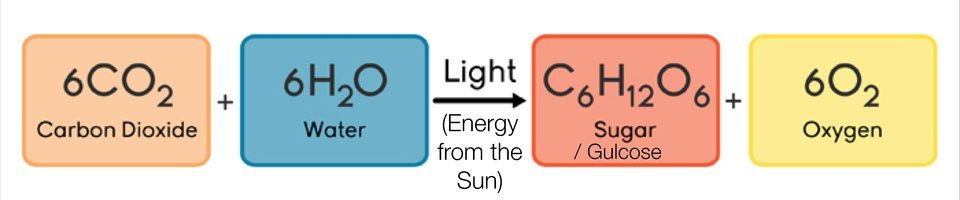
The equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H20 --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Written out, the equation is: 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water --> glucose + 6 oxygen The energy transformation for photosynthesis is: Light energy --> chemical energy (in glucose) The glucose that is made during photosynthesis can then be used by the plant for energy or for growth. |
Chemical Formula for Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants turn carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into carbohydrates (plant tissue), using light as an energy source and releasing oxygen as a byproduct. Photosynthesis is one of the most important biological processes on Earth: It makes air breathable, and supplies most of the energy required for all life forms. © Science Media Group. |
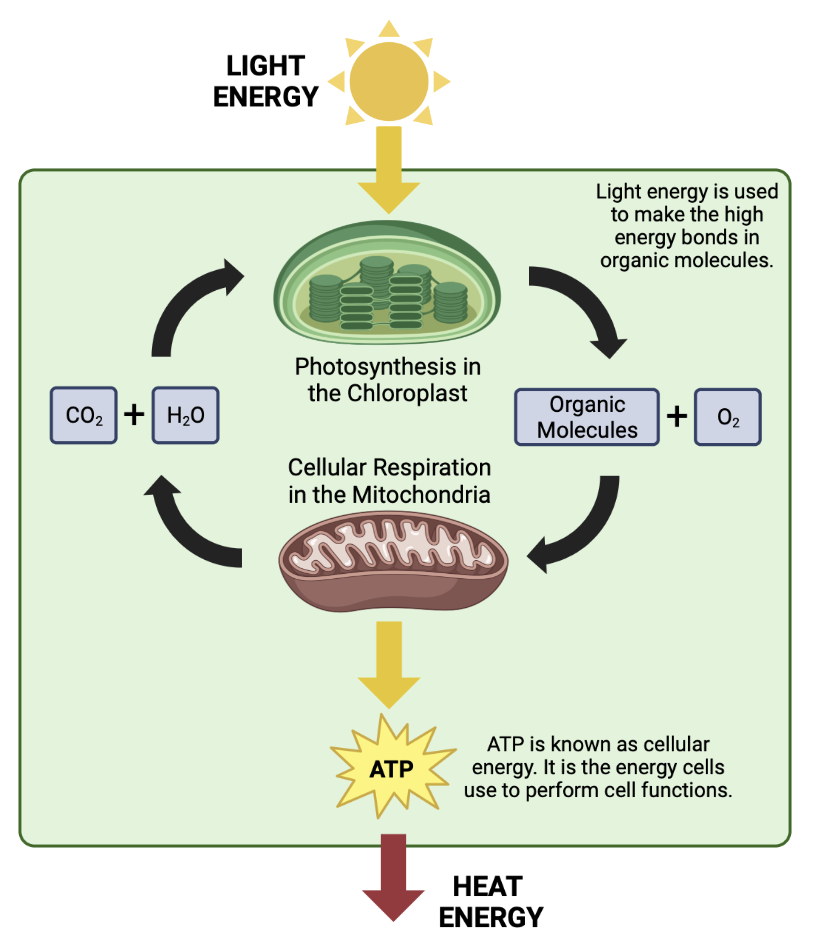
Cellular RespirationCellular respiration in plants is just like cellular respiration in animals. Plant cell, like animal cells, have mitochondria. The mitochondria are organelles that perform cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process that living things use to get energy.
The equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H20 Written out, the equation is: glucose + 6 oxygen --> 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water The glucose for cellular respiration in plants comes from photosynthesis. When the plants use the glucose and oxygen they make carbon dioxide and water. The process of photosynthesis is the opposite of the process of cellular respiration. The energy transformation for cellular respiration is: chemical energy (in glucose) --> chemical energy (in ATP) --> heat energy ATP is a molecule that the cell can use to transport energy from the mitochondria to other parts of the cell. If the cell needs energy to perform a task - like transporting salt into the cell - the ATP made in the mitochondria, during cellular respiration, can move to the area of the cell that is transporting salt and the ATP can release the energy for the cell to use. The energy that is stored in ATP is converted into heat energy. |
Biosynthesis
|
Glucose, made during photosynthesis, can also be used by the plant for growth. Plant cells, like animal cells, are made of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. To make these molecules, plants can use glucose in order to build the larger molecules that the plant cell uses to grow and replicate. Turning small molecules (monomers) into large molecules (polymers) is called biosynthesis.
|
How do we know?
Plants do photosynthesis - when placed in the light, plants do photosynthesis. We know this because when we put a plant into a container with BTB and leave it in the light the BTB turns blue. This means that carbon dioxide is being pulled out of the air.
Plants do cellular respiration - At night, plants are still performing cell functions that require energy. They get this energy from cellular respiration. We know this because when you put a plant into a container with some BTB overnight the BTB will turn yellow. This means the plant is releasing carbon dioxide. The container will also have a lot of condensation on it. This is because the plant is releasing water as waste during cellular respiration.
Plants need light to do photosynthesis - the plant placed in the dark will not cause the BTB to turn blue because the plant cannot do photosynthesis in the dark. Also, when a portion of the leaf is covered, it will not make starch. Starch is made out of glucose and if they leaf cannot make glucose then it cannot make starch. Only the leaves the receive light will make glucose and then starch. This is also how we know that plants can do biosynthesis because starch is made by putting two or more sugar molecules together.
Plants do cellular respiration - At night, plants are still performing cell functions that require energy. They get this energy from cellular respiration. We know this because when you put a plant into a container with some BTB overnight the BTB will turn yellow. This means the plant is releasing carbon dioxide. The container will also have a lot of condensation on it. This is because the plant is releasing water as waste during cellular respiration.
Plants need light to do photosynthesis - the plant placed in the dark will not cause the BTB to turn blue because the plant cannot do photosynthesis in the dark. Also, when a portion of the leaf is covered, it will not make starch. Starch is made out of glucose and if they leaf cannot make glucose then it cannot make starch. Only the leaves the receive light will make glucose and then starch. This is also how we know that plants can do biosynthesis because starch is made by putting two or more sugar molecules together.
|
|
|
Proudly powered by Weebly