Header Image Attribution: Migs Reyes, pexels.com
Pedigree Analysis
A pedigree is a visual representation or diagram of a family's genetic history over several generations. It is used in genetics to track the inheritance of specific traits or diseases within a family and understand patterns of inheritance.
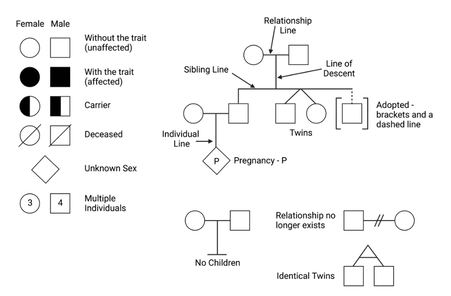
In a pedigree, different shapes and symbols are used to represent individuals and their relationships. Here are the common symbols used in a pedigree:
Specific traits or conditions of interest, such as eye color, blood type, or a genetic disorder, are often indicated in the pedigree. Each individual's phenotype (observable traits) and sometimes genotype (genetic makeup) are included.
By examining a pedigree, geneticists can identify patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, or X-linked recessive. They can also use pedigrees to determine the likelihood of certain traits or diseases being passed on to future generations.
Pedigrees are valuable tools in genetic counseling, medical research, and the study of hereditary diseases. They allow scientists and healthcare professionals to trace the genetic history of families, predict the probability of certain conditions occurring, and provide information and guidance to individuals and families about their genetic risks and choices.
A pedigree is a visual representation or diagram of a family's genetic history over several generations. It is used in genetics to track the inheritance of specific traits or diseases within a family and understand patterns of inheritance.
In a pedigree, different shapes and symbols are used to represent individuals and their relationships. Here are the common symbols used in a pedigree:
- Square: Represents a male individual.
- Circle: Represents a female individual.
- Line connecting a square and a circle: Represents a marriage or union between a male and a female.
- Horizontal line: Represents offspring (children) of the parents, listed from left to right in their birth order.
- Vertical line from a parent to the offspring: Represents the parent passing on genetic information to the child.
Specific traits or conditions of interest, such as eye color, blood type, or a genetic disorder, are often indicated in the pedigree. Each individual's phenotype (observable traits) and sometimes genotype (genetic makeup) are included.
By examining a pedigree, geneticists can identify patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, or X-linked recessive. They can also use pedigrees to determine the likelihood of certain traits or diseases being passed on to future generations.
Pedigrees are valuable tools in genetic counseling, medical research, and the study of hereditary diseases. They allow scientists and healthcare professionals to trace the genetic history of families, predict the probability of certain conditions occurring, and provide information and guidance to individuals and families about their genetic risks and choices.
|
|
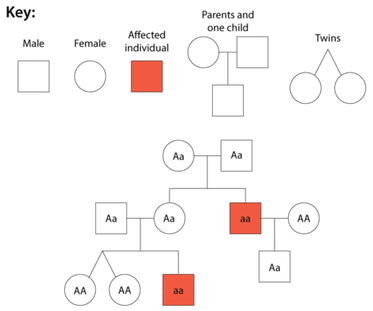
In a pedigree, squares symbolize males, and circles represent females. A horizontal line joining a male and female indicates that the couple had offspring. Vertical lines indicate offspring which are listed left to right, in order of birth. Shading of the circle or square indicates an individual who has the trait being traced. In this pedigree, the inheritance of the recessive trait is being traced. A is the dominant allele, and a is the recessive allele.
Image attribution: Zachary Wilson, CK-12 Foundation, CC BY-NC 3.0 |
Proudly powered by Weebly